The Chinese Civil War lasted for a very long time; it went on for more than 25 years between the Communist Party of China and the government of China. At the time, the government of China was represented by the nationalist party and called the Kuomintang. Although this war was interrupted in the middle, it was not a peaceful break for the Chinese People.
The Chinese War went on from 1927 to 1936 until it was stopped as a result of the Japanese invasion of China. Then, World War II broke out in 1939. After World War II ended and Japan was defeated, the two dedicated Chinese parties picked up where they left off and continued their civil war for the control of China.
How the Chinese Civil War began
After almost three centuries of ruling China, the Qing Dynasty collapsed in 1911, which left an opportunity for power where the dynasty once ruled. The two largest and most powerful parties in China, the communist party (CPC) and the nationalist party (KMT), decided to unite their powers against the warlords. The warlords controlled multiple areas of China. At this time, the Soviet Union helped both parties in their mission to fight off the warlords.
However, as the two parties continued an effort to collaborate to defeat a common enemy, tension grew between them. This tension turned into an official civil war in 1927 when the leader of the nationalist party, Chiang Kai-shek, decided to kill and capture most of the communist party leaders in what is known today as the Shanghai Massacre.
This massacre led the leader of the communist party, Mao Zedong, to start an uprising against the nationalist government. Mao called the uprising the Autumn Harvest Uprising. The uprising was a failure, however, it was the event that started the civil war.
A decade of war
The next ten years of the Chinese People’s lives were nothing but war. The common people were led by the communist party and Mao Zedong, which was now known as the CPC army. The CPC army fought against the rule of the Kuomintang, or the nationalist party, over the control of China. They fought from 1927 to 1936.
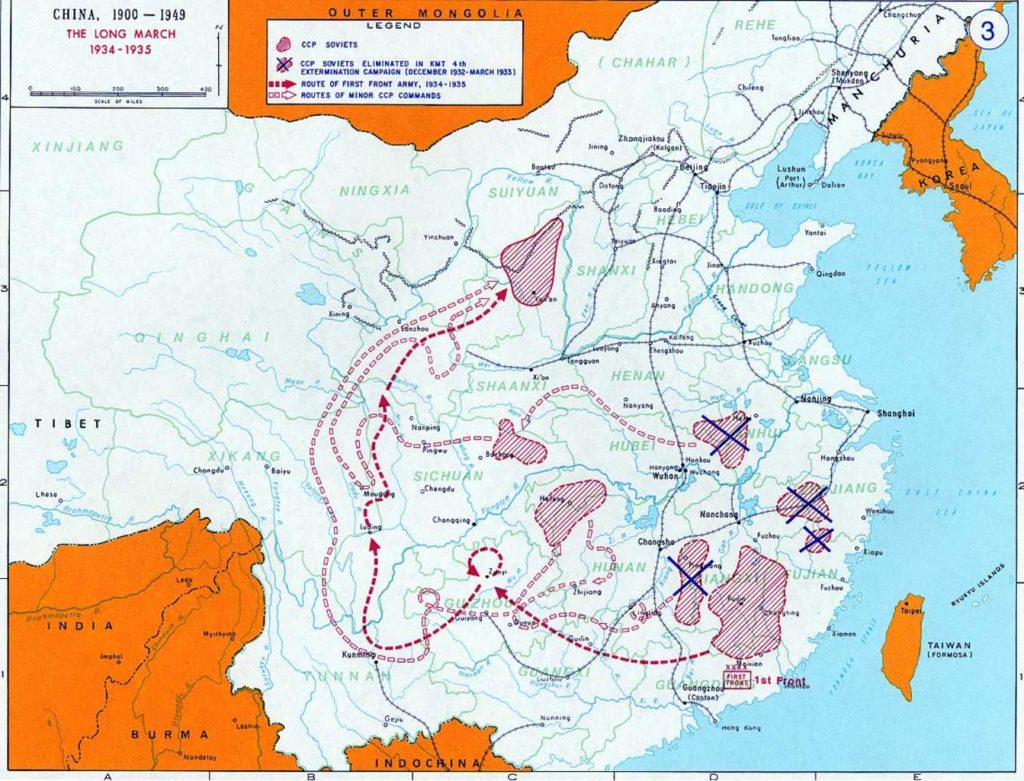
In 1934, the Kuomintang seemed to be winning the Chinese Civil War. They succeeded in forcing the CPC army to retreat and start a long march that lasted an entire year. The CPC army had to march 7,000 miles from Jiangxi province in south China to Shaanxi province in north China. The march started in October 1934 with 80,000 soldiers in the CPC army. It ended in October 1935 with only 8,000 soldiers remaining in the communist army.
Stopped by a bigger threat
Once again, the two fighting sides had to unite their fronts when Japan invaded China in 1936. The two parties chose to put their differences aside and fight against their common enemy. However, after years of civil war, they were unable to trust each other even when they united against the Japanese.
The Chinese Civil War starts again!
Once the Japanese threat was ended by Japan’s defeat in World War II, the two Chinese parties, CPC and KMT resumed their own civil war. This time, however, the Chinese Civil War was a part of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union. The U.S. supported the nationalist party (KMT), while the Soviet Union supported the communist party, helping them get the weapons that the Japanese left when they retreated from China.
The United States tried for years to make peace in China by splitting the country into two halves. The thought was that each party would control one half, but neither side would agree to those terms.
How the Chinese Civil War ended
From 1945 to 1948, both sides had almost equal strength in the war. As the year 1948 came, however, the CPC started to win control over more cities and gain more support from the Chinese people. In 1949, the CPC managed to take over the city of Beijing, the capital of China. They announced the country of China to be under the control of the communist party and named it the People’s Republic of China.
Back to Cold War topics
